Service是一种计算型组件,用于在后台执行一系列的计算任务。由于工作在后台,因此用户是无法直接感知到它的存在。Service组件和Activity组件略有不同,Activity组件只有一种运行模式,即Activity处于启动状态,但是Service组件却有两种状态:启动状态和绑定状态。当Service组件处于启动状态时,这个时候Service内部可以做一些后台计算,并且不需要和外界有直接的交互。
Service分为两种工作状态,一种是启动状态,主要用于执行后台计算,另一张是绑定状态,主要用于其他组件和Service的交互,需要注意的是Service的这两种状态是可以共存的,即Service既可以处于启动状态也可以同时处于绑定状态。
Service的启动过程 Service的启动过程从ContextWrapper的startService开始。
1 2 3 4 @Override public ComponentName startService (Intent service) { return mBase.startService(service); }
这里的mBase的类型是ContextImpl,其实说到这,就得说下Activity被创建时会通过attach方法将一个ContextImpl对象关联起来,这也就是mBase。从ContextWrapper的实现可以看出,其中大部分操作都是通过mBase来实现的,在设计模式中这是一种典型的桥接模式。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 @Override public ComponentName startService (Intent service) { warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess(); return startServiceCommon(service, mUser); } private ComponentName startServiceCommon (Intent service, UserHandle user) { try { validateServiceIntent(service); service.prepareToLeaveProcess(this ); ComponentName cn = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().startService( mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), service, service.resolveTypeIfNeeded( getContentResolver()), getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier()); if (cn != null ) { if (cn.getPackageName().equals("!" )) { throw new SecurityException ( "Not allowed to start service " + service + " without permission " + cn.getClassName()); } else if (cn.getPackageName().equals("!!" )) { throw new SecurityException ( "Unable to start service " + service + ": " + cn.getClassName()); } } return cn; } catch (RemoteException e) { throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
从startServiceCommon方法中可以看出,是ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()这个方法的类启动的,其实ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()就是AMS,是通过AMS来启动服务的行为是一个远程过程调用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 @Override public ComponentName startService (IApplicationThread caller, Intent service, String resolvedType, String callingPackage, int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException { enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startService" ); if (service != null && service.hasFileDescriptors() == true ) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("File descriptors passed in Intent" ); } if (callingPackage == null ) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("callingPackage cannot be null" ); } if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "startService: " + service + " type=" + resolvedType); synchronized (this ) { final int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid(); final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid(); final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); ComponentName res = mServices.startServiceLocked(caller, service, resolvedType, callingPid, callingUid, callingPackage, userId); Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId); return res; } }
在上面的代码中,AMS会通过mServices这个对象来完成Service后续的启动过程,mServices对象的类型是ActiveService,ActiveService是一个辅助AMS进行Service管理的类,包括Service的启动、绑定和停止等。
最终是通过app.thread的scheduleCreateService方法来创建Service对象并调用onCreate,接着再通过sendServiceArgsLocked方法来调用Service的其他方法,比如onStartCommand,这两个过程均是进程间通信,到最后是通过ApplicationThread的scheduleCreateService方法来
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public final void scheduleCreateService (IBinder token, ServiceInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) { updateProcessState(processState, false ); CreateServiceData s = new CreateServiceData (); s.token = token; s.info = info; s.compatInfo = compatInfo; sendMessage(H.CREATE_SERVICE, s); }
是通过发消息给Handler H,H会接收这个CREATE_SERVICE消息并通过handleCreateService方法来完成Service的最终启动。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 private void handleCreateService (CreateServiceData data) { unscheduleGcIdler(); LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck( data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo); Service service = null ; try { java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader(); service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance(); } catch (Exception e) { if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) { throw new RuntimeException ( "Unable to instantiate service " + data.info.name + ": " + e.toString(), e); } } try { if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Creating service " + data.info.name); ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this , packageInfo); context.setOuterContext(service); Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false , mInstrumentation); service.attach(context, this , data.info.name, data.token, app, ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()); service.onCreate(); mServices.put(data.token, service); try { ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting( data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0 , 0 ); } catch (RemoteException e) { throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer(); } } catch (Exception e) { if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) { throw new RuntimeException ( "Unable to create service " + data.info.name + ": " + e.toString(), e); } } }
handleCreateService主要完成了如下几件事:
通过类加载器创建Service的实例
创建Application对象并调用其onCreate,当然Application的创建过程只会有一次。
接着创建ConTextImpl对象并通过Service的attach方法建立二者之间的关系。
最后调用onCreate方法,并将Service对象存储到ActivityThreadd的一个列表中。
Service的绑定过程 和Service的启动过程一样,Service绑定过程也是从ContextWrapper开始的。
1 2 3 4 5 @Override public boolean bindService (Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags) { return mBase.bindService(service, conn, flags); }
然后会调用bindServiceCommon方法,这个方法主要完成如下两件事情:
首先将客户端的ServiceConnection对象转化为ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection对象。
接着bindServiceCommon会通过AMS来完成Service的具体绑定过程,对应于AMS的bindService方法。
最终也是调用handleBindService来处理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 private void handleBindService (BindServiceData data) { Service s = mServices.get(data.token); if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG, "handleBindService s=" + s + " rebind=" + data.rebind); if (s != null ) { try { data.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader()); data.intent.prepareToEnterProcess(); try { if (!data.rebind) { IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent); ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService( data.token, data.intent, binder); } else { s.onRebind(data.intent); ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting( data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0 , 0 ); } ensureJitEnabled(); } catch (RemoteException ex) { throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer(); } } catch (Exception e) { if (!mInstrumentation.onException(s, e)) { throw new RuntimeException ( "Unable to bind to service " + s + " with " + data.intent + ": " + e.toString(), e); } } } }
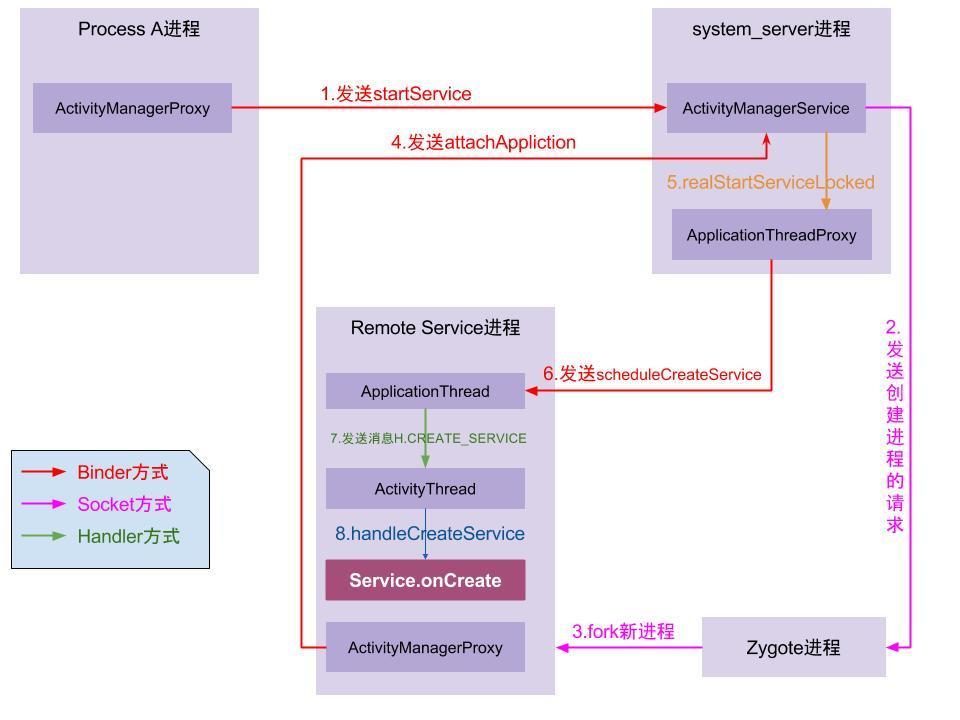
最后,以借用一张流程图来说明: